Compact water purification system for PEM electrolyzers in green hydrogen production, processing up to 30 l/hour. Guaranteed purity, space efficiency, and easy maintenance make it ideal for hydrogen electrolyzers producing up to 30Nm³/h.
Overview
While conventionally treated water can be used for various industrial and energy generation processes, in green hydrogen production, the ions, particles and organics present in this water have the potential to adhere to the surface of an electrode, catalyst or membrane in the proton electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolyzer. This risks reducing process efficiency, causing damage or shortening equipment lifespan.
For efficient green hydrogen production, a consistent supply of purified water is essential, and water must undergo an extra stage of treatment. Purenergy 30 is used in the electrolysis stage of green hydrogen production to provide purified water for the proton electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolyzer process.
How does Purenergy 30 work?
Developed by Elga Labwater — a subsidiary of Veolia Water Technologies — Purenergy 30 is the first water purification system specifically designed for the green hydrogen production industry and represents a step-change in purification standards in this sector. Purenergy uses three key water purification technologies:
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is the first stage of the water purification system and uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove ions, particles, organics and larger particles from water. The water is pressurized and forced through the membrane, separating contaminants from the clean water.
Electrodeionization stack
Electrodeionization (EDI) is a water purification process that combines ion exchange and electrodialysis to produce high-purity water. The EDI stack comprises a set of chambers filled with ion-exchange resins separated by ion-exchange membranes. Where the water enters the stack, an electrical field is applied at right angles to the flow, forcing ions to move through the resins and across the membranes. These impure ions are collected into concentrate streams which are then drained.
Ultraviolet light treatment
The final stage of the Purenergy 30 water purification system is ultraviolet (UV) light treatment. UV disinfects the water in a chemical-free way that effectively destroys any remaining bacteria, viruses, or pathogens left in the water after the ions and particles have been removed.
UV disinfection is commonly used in various applications and is considered a reliable and environmentally friendly method to purify water as it does not introduce any chemicals into the water or produce harmful disinfection byproducts.
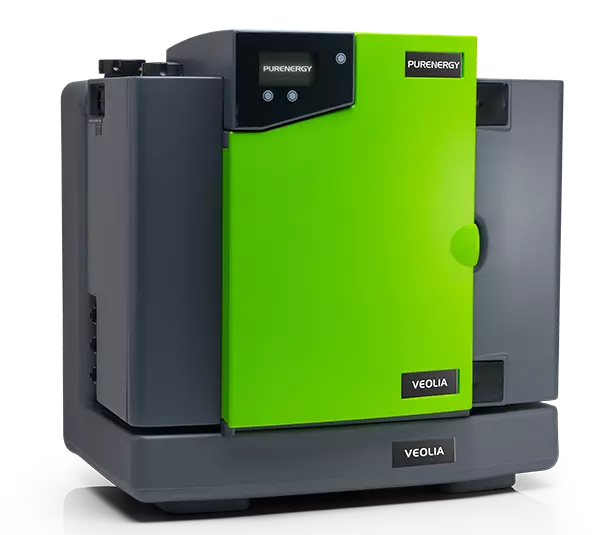

Features and benefits

Compact
550mm wide and 460mm high. Wall mountable, optional docking vessel — saving valuable space.
Reliable
Extensive experience in mission-critical environments means reliability is tested, proven and unrivaled.
Guaranteed water purity
Regular recirculation through the system’s purification technologies ensures the water specification is maintained.

Eco-aware
The EDI (electrodeionization) technology minimizes environmental impact.

Easy to use
A near plug-and-play installation process combined with automated monitoring and alarms enables a simple set-up and operation.

Simple maintenance
The expertise gained from a global installed base delivers an easily serviceable unit.
Applications
Services
Contact
We are committed to providing the green hydrogen production industry with the tools it needs to achieve excellence in quality control processes. We are proud to contribute to the advancement of green hydrogen production while maintaining the highest standards of regulatory compliance. Purenergy 30 represents a step change in water purification standards.

Ahmed Elshorbagy
Business Development Manager, Veolia Water Technologies Middle East
Contact Ahmed through his LinkedIn account
FAQ about Purenergy 30
What is green hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is hydrogen gas produced by splitting water molecules through electrolysis, using renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power.
In simple terms, the process is in three parts:
- Renewable energy generation: Electricity is generated from renewable sources such as solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines or hydroelectric dams.
- Electrolysis: The renewable electricity is then used to power an electrolyzer, which splits water molecules (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) through the process of electrolysis. This is typically done in a proton electrolyte membrane (PEM) or an alkaline electrolyzer.
- Hydrogen production: Hydrogen (H2) is collected as the product of the proton electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolysis process, while oxygen (O2) is released as a byproduct.
Green hydrogen gas can be used in a wide range of sectors such as transportation, industrial production and power generation. It is particularly useful for sectors where direct electrification may be challenging or impractical, such as long-haul transportation, heavy industry and energy storage applications requiring high energy density and long-duration storage capabilities.
Why is green hydrogen important?
Decarbonization: Unlike hydrogen produced from fossil fuels, green hydrogen production emits little to no greenhouse gases, making it a crucial tool in efforts to decarbonize various sectors of the economy. It helps reduce overall carbon emissions, mitigating climate change and contributing to net zero emissions.
Energy storage: Excess electricity generated from renewable sources during times of low demand or high availability can be used to produce green hydrogen. The hydrogen can then be stored and later converted back into electricity providing a reliable and flexible means of balancing energy supply and demand and enhancing grid stability.